Optimizing Post-workout Recovery: What We Get Wrong
In the pursuit of peak physical performance, athletes and fitness enthusiasts often find themselves pushing their bodies to the limit. However, without proper recovery, this intense training can lead to a state known as Overtraining Syndrome (OTS). In this blog post, we'll explore the stages of the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS), delve into the potential risk factors associated with OTS, and discuss the critical role of post-workout nutrition for efficient recovery.
Understanding Overtraining Syndrome:
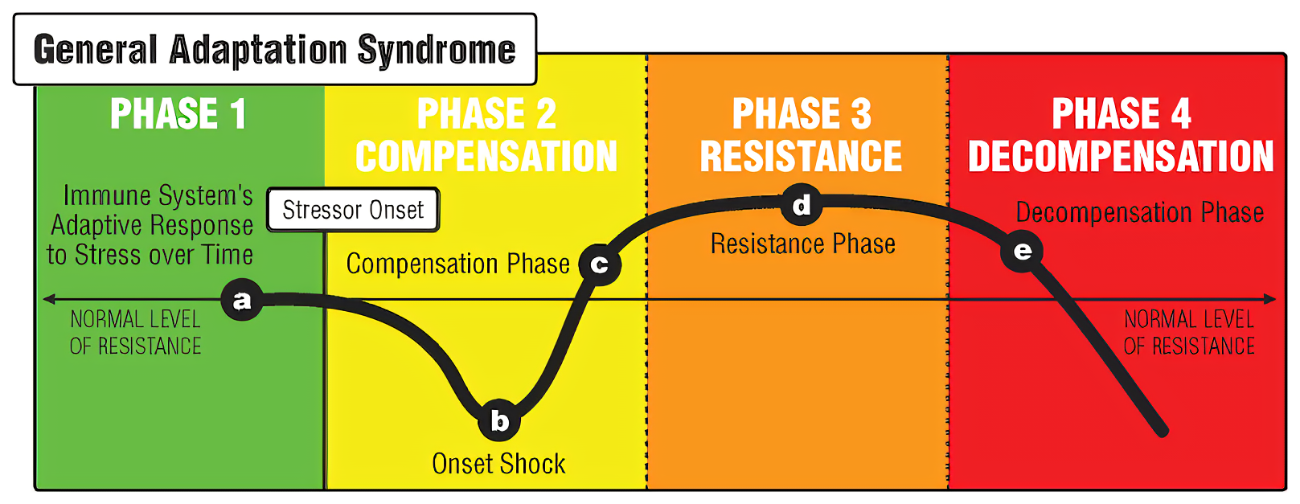
The General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) proposed by Hans Selye helps us comprehend the body's response to stress. In the context of physical training, Overtraining Syndrome represents a state of prolonged stress, manifesting as fatigue, decreased performance, muscle soreness, and increased susceptibility to illness.
Potential Risk Factors:
- Increased Injury Risk: Inadequate recovery can lead to compromised biomechanics and an increased risk of injuries.
- Decreased Performance: Overtraining may result in plateaued or declining strength gains and diminished overall fitness levels.
- Compromised Immunity: Chronic stress from insufficient recovery suppresses the immune system, making individuals more prone to infections.
- Sleep Disturbances: Overtraining can contribute to difficulties falling and staying asleep, impacting overall well-being.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Intense training without adequate recovery may disrupt hormonal balance, affecting muscle growth, recovery, and overall health.
- Less Enjoyment & Drive: Inadequate recovery may lead to decreased motivation and enjoyment of training sessions.
The Role of Post-Workout Nutrition:
Effective recovery involves a combination of proper nutrition and supplementation. Key factors include:
- Protein Timing: While total protein intake is crucial, essential amino acids (EAAs) are absorbed more quickly than whey isolate, stimulating protein synthesis faster.
- Carbohydrates: Timing is crucial for replenishing muscle glycogen. Carbs, along with creatine, can lead to glycogen super-compensation, driving nutrients into depleted muscles.
- Insulin Response: Carbohydrates induce an insulin spike, facilitating glycogen and nutrient transport into muscle cells, promoting recovery and reducing muscle protein breakdown.

Introducing Titan Nutrition ReBUILD™:
This revolutionary post-workout supplement challenges the conventional wisdom of recovery. Key complexes and ingredients include:
- Glycolytic Transport Complex: Enhances insulin sensitivity for superior glycogen and nutrient transport.
- Amino Construction Complex: Rapid absorption of EAAs for immediate post-workout recovery.
- Creatine Recovery Complex: Combines carbohydrates and creatine for glycogen super-compensation and ATP store replenishment.
- Hydro-Electrolyte Complex: Optimizes cellular hydration and muscular function.
- Antioxidant Protect Complex: Fights off harmful free radicals generated during intense exercise.
Who Benefits from ReBUILD™?
ReBUILD™ is designed for a wide range of individuals, including athletes, those engaged in strength training and H.I.I.T., and fitness competitors from various disciplines (bodybuilding, CrossFit, powerlifting, etc), providing comprehensive post-workout recovery.
Understanding and preventing Overtraining Syndrome requires a holistic approach to training, recovery, and nutrition. With the right strategies, including the use of advanced supplements like Titan Nutrition ReBUILD™, individuals can optimize their recovery and unleash their full physical potential, and optimize their ROI from grueling training sessions.

 Log in
Log in


